ASIA
PACIFIC INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY

A BUSINESS PROCESS REENGINEERING INITIATIVE FOR MOUNT SHIPPING
PVT. LTD.
SUBMITTED TO : MR. SYED REHAN SUBJECT : BUSINESS PROCESS REENGINEERING SUBMITTED ON : 14th
OF MAY 2004 INTAKE : GF0421COM/BIT FULL-TIME GROUP MEMBERS : LALINDRA
FERNANDO (CB001238) PREMESH
SILVA (CB001070) THILANKA
SENARATNE (CB001213) UPAKE
DE SILVA (CB001107)
F
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Table
of Contents
TABLE OF CONTENTS
3.0 MISSION, VISION
AND OBJECTIVES
3.1 Roles and
Responsibilities
6.0 ADOPTING AN
ORGANIZATIONAL HORSEPOWER STRATEGY
8.0 BPR METHODOLOGY
COMPARISON
8.5 Justification
of the Chosen Methodology
9.1 Cause and
Effect Diagram (Fishbone)
9.4 AS-IS Process
Mapping Diagram
9.5 Processes
Identified for Reengineering
10.0 TOOL USED FOR
REENGINEERING
11.2 To-Be Process
Mapping Diagram Inquiry Handling and Documentation
15.0 BACKUP AND
CONTINGENCY PLAN
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Our sincere appreciation goes out to the
following persons, all of whom helped to make this project a sensational
success.
·
Mr. Syed Rehan for
guiding us and elucidating the predicaments encountered.
·
Mr. Hasitha
Wijeygunawardane and his competent team of lab assistants for providing us with
lab facilities and other technical support at all times.
·
All our colleagues
for their continuous support and encouragement without which this project would
not have been a success.
ABSTRACT
Mount Shipping Pvt. Ltd., which is a freight-forwarding
firm that primarily ships garments to the USA, was the chosen company for the
Business Process Reengineering initiative. A fresh firm to the freight
forwarding market, it has started out small and is struggling to compete with
the veterans.
After a thorough analysis of the firms’
processes and procedures, a few processes were chosen to undergo the
reengineering improvement. Strategic analysis tools revealed that a wide
assortment of external factors influences the freight forwarding industry. Based
on all these factors a suitable BPR methodology was chosen after a comparison
with the available methodologies, to improve the processes and achieve the
objectives of the company.
Several tools were used to analyse the processes
of the current system (AS-IS). These tools revealed the extent to which
reengineering should take place and the processes were identified and mapped
accordingly. The tools showed that by cutting down redundant, repetitive, and
decision-making time-consuming tasks, the effectivity and efficiency of the
firm would be dramatically improved.
Based on the AS-IS, the visualised TO-BE
processes were developed. Information Technology solutions were incorporated
into the TO-BE processes to create innovative value added processes for the
specific functional areas in order to compete with the best of the freight
forwarders.
1.0
INTRODUCTION
The BPR team members decided to investigate a relatively unknown freight-forwarding firm known as Mount Shipping. A thorough investigation and analysis revealed that the firm’s processes and procedures were convoluted as no particular staff member had a specific list of activities to be carried out.
The remainder of this document depicts the
approach taken to reengineer Mount Shipping.
After stating the firm’s mission, vision and
objectives, there are various external factors observed that influence the
performance of the business. This leads to the OHP and benchmarking analysis plus
the selection of the business process reengineering methodology.
An assortment of techniques would be shown, to
map the AS-IS processes and the enhanced TO-BE processes would be followed.
Finally, the costs of the implementation would
be calculated and the reengineering effort concluded.
2.0 COMPANY BACKGROUND
Mount Shipping Overview
Mount Shipping Agencies (Pvt) Ltd is a company that provides a comprehensive range of freight solutions to customers who require both national and international services. It provides Sea freight as well as Airfreight services to various destinations around the globe. The company is also involved in handling inbound cargo. It is a company whose key goal is customer service.
The company has the following departments:
Marketing Sales, Operations, documentation / Customer service, Finance and Administration. There are 9 employees who carry out the day to day operations.
The company office is situated in Colombo 03.
The Airfreight department handles all types of cargo such as general, perishable, dangerous and garments on hangers (GOH). It also offers sea / air service through the gateways of Dubai for cargo destined to United States, Europe and Scandinavian destinations. The Airfreight department has very close ties with the all-major airlines offering services out of Colombo.
Mount Shipping has their nominated container freight station, which is well equipped with modern facilities. The company has a n experienced wharf department which looks into clearing of import cargo and forwarding of export cargo. The company holds the license issued by Sri Lanka Customs and Sri Lanka Ports Authority to carry out as customs house agents.
Mount
Shipping has to use the following shipping lines and their respective yards to
ensure the goods are shipped to the desired destination:
Shipping Agents
- Lloyd Serendib Ltd.
- Lucky Seaworld Services (Pvt) Ltd.
- M A Razak & Company Ltd.
- Mackinnon Mackenzie & Co
(Shipping) Ltd.
- Maersk Lanka (Pvt) Ltd.
- Malship (Ceylon) Ltd.
- Marine International Agencies (Pvt)
Ltd.
- Maritime Agencies Ltd.
- Maritime Lanka Ltd.
- Asha Shipping Pvt. Ltd.
Mass
Logistics & Shipping (Pvt) Ltd
3.0 MISSION, VISION AND OBJECTIVES
A strategic plan commences with a
clearly defined business mission.
Mintzberg defines a mission as
follows:
“A mission
describes the organization’s basic function in society, in terms of the
products and services it produces for its customers”.
Mount Shipping’s Mission statement:
“We provide a comprehensive range of
freight solutions to customers requiring both national and international
services. We believe that our customers have a right to expect a reliable
service which is both secure and cost effective.”
Mount Shipping claims that they are
committed to providing an efficient, competitive and flexible service, which
meets the individual needs of the customer.
To succeed in the long term, the
business needs a vision of how they will change and improve in the future. The
vision gives the business the impetus and motivation for employees. It helps
set the direction of corporate and marketing strategy.
Davidson
identifies six requirements for an effective business vision:
1.
Provide future direction
2.
Express a consumer benefit
3.
Be realistic
4.
Be motivating
5.
Must be fully communicated
6.
Consistently followed and measured
A clear business mission should have
each of the following elements:
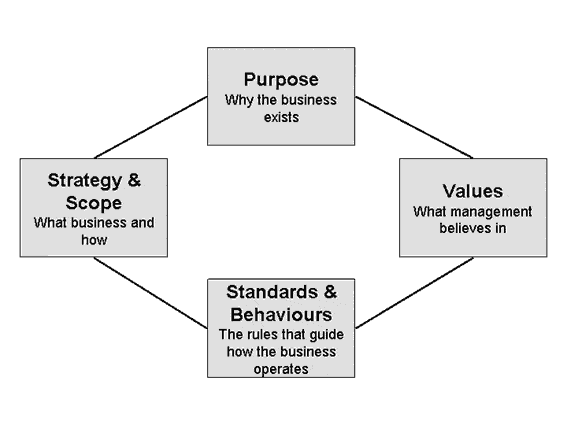
Purpose
The
business exists in order to provide a service to the garment exporting
industries of Sri Lanka.
A
Strategy and Strategic Scope
The
mission statement provides the commercial logic for the business and defines
the following 2 components:
1.
The services it offers (and
therefore its competitive position)
2.
The competences through
which it tries to succeed and its method of competing
A
business’ strategic scope defines the boundaries of its operations. These are
set by management.
The
decisions that the management makes about the strategic scope define the nature
of the business.
Policies
and Standards of Behaviour
The
organization should conform to the mission statement by making it a part of its
everyday operations. Examples include handling inquires, positive feedback and
updating the client on a regular basis.
Values
and Culture
The
values of a business are the basic, often un-stated, beliefs of the people who
work in the business. These would include:
·
Business principles –
commitment to the customers
·
Loyalty and commitment –
loyalty to the staff and personal sacrifices made for the business.
·
Guidance on expected behaviour
– a strong sense of mission helps create a work environment where there is a
common purpose
Objectives
Objectives set out what the business is trying
to achieve.
Objectives can be set at two levels:
1. Corporate level
These are objectives that concern the business
or organisation as a whole
Objectives of Mt. Shipping:
·
A
high return on investment
·
A
50% increase in operating profit
·
A
10% increase in the earning per share
2. Functional level
·
Aim
to build a customer database of around 2500 in the next 12 months.
·
Aim
to achieve a market share of about 10%
·
Aim
to achieve 75% of customer awareness of the service.
3.1 Roles
and Responsibilities
|
Job Title |
Task |
|
Mr. Anujath Fernando (Manager) |
Oversees the entire operation |
|
Marketing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Job Title |
Task |
|
Mrs. Nirmalee Subasinghe (Asst Manager Documentation) |
Export Cargo – Release of Bill of Lading |
|
Import Cargo – Release of Delivery Order |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Job Title |
Task |
|
Mr. H. Wimalaratne (Accountant) |
Handling the finances of the company |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Job Title |
Task |
|
Mr. Pradeep Fernando (Shipping Assistant) |
Handling LCL consolidations and MCC operations / Transhipment cargo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Job Title |
Task |
|
Mr. Shiraj Martin (Manager Operations) |
Managing the Wharf department |
|
Managing the equipment controller |
|
|
Managing the port operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Job Title |
Task |
|
Mr. Dishan Kumarawansa (Shipping Assistant Air Freight Operations) |
Handing over of air cargo to airport(Katunayake) |
|
Certifying of weights and dimensions with factories |
|
|
Preparations of house Airway bills |
|
|
Sending instructions to airlines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Job Title |
Task |
|
Mr. Roshan Habadilwewa (Equipment Controller) |
Monitoring the controller |
|
Coordinating with the surveyors |
|
|
Coordinating with the container yard |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. 0 THE ORGANISATIONAL CHART
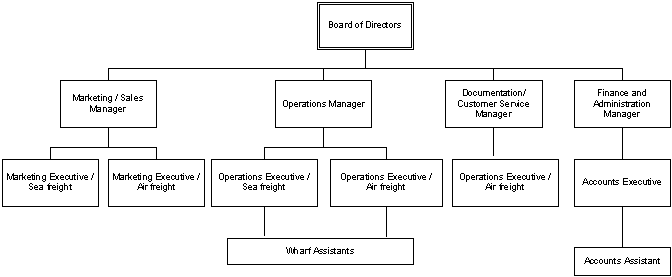
5.0 STRATEGIC ANALYSIS
Johnson and Scholes define strategy
as follows:
"Strategy is the direction and
scope
of an organisation over the long-term: which achieves advantage for the organisation through
its configuration of resources within a challenging environment, to meet the needs of markets and
to fulfill stakeholder
expectations".
Strategic analysis is mainly about
analyzing the strength of the businesses' position and understanding the
important external factors that may influence that position. The process of
Strategic Analysis can be assisted by a number of tools such as PEST and SWOT.
5.1 PEST ANALYSIS
PEST
analysis is a marketing tool that is used to analyze the organization’s
environment and how the to cater to the drivers. The organization's marketing
environment is made up from:
1. The
internal environment – the staff (or internal customers), office technology,
wages and finance
2. The
micro-environment - external customers, agents and distributors, suppliers, the
competitors.
3. The
macro-environment - Political (and legal) forces, Economic forces,
Sociocultural forces, and Technological forces. These are known as PEST factors.
Political
Factors
The
political arena has a huge influence upon the regulation of the business and
the spending power of consumers and other businesses.
Due to
the civil war, which has been waging for over 20 years and the terrorist
activities in the Central Business Districts (CBD), the government has been
fairly unstable. However, due to the peace process the government was on its
way to achieving relative stability; this was disrupted when the opposition
came into power. Consequently, resulting in a highly unstable government since
the winning party has not got the majority of votes. Thus, the political future
of the country is uncertain.
There
is no clear government policy. It is a mixed economy where the trading is run
by the government.
The government
is not very concerned with culture and religion.
Thus,
Mount Shipping would be affected by the political situation due to the exports
carried out and the relations with the other countries.
Economic
Factors
The
trading economy in the short and long-term should be considered in order to
carry out marketing.
The
interest rates are falling because the government would like the public to
invest. There is less borrowing done from the commercial banks.
The
level of inflation is at a steady rate at the moment.
These
are good signs for Mount Shipping, thus, they should increase their marketing.
Socio-cultural
Factors
The
social and cultural influences on business have an influence on the Sri Lankan
public.
Buddhism
is the dominant religion.
The
Sri Lankan consumers embrace foreign goods. They highly prefer anything foreign
to Sri Lankan made as their notion is that Sri Lankan products are lower in
quality and standards than the foreign products.
Leisure
time is quite plentiful amongst the Sri Lankan working environment due to the
holidays that cater to the major religions. This gives the consumer some time
to select the best possible service and/or product available.
The
male role is dominant within the Sri Lankan society. However, female dominance
is on the rise. The older generation is quite a significant part of the Sri
Lankan population. They seem to be living longer and more prosperously.
Mount
Shipping should take these factors into consideration.
Technological
Factors
Technology
is vital for competitive advantage, and is a major driver of globalization.
Technology
improves the standard of quality of products and enables them to be produced at
a lower cost thus increasing profits.
The
technologies that have exploded into the Sri Lankan market have offered
consumers and businesses more innovative products and services such as Internet
banking, WAP, SMS Banking and 3G Mobile technologies. There has been a boom in
the wireless and mobile industry during the last couple of years.
E-commerce
in Sri Lanka is currently at an infancy stage. This is due to the fact that
only a small percentage of Sri Lankans have the necessary technology to shop
online. The basic requirements of a computer, Internet connection and credit
cards are absent. Only certain classes of Sri Lankans have the necessary
requirements.
However,
the ADSL broadband technology (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) has been
introduced in the past few months to the city of Colombo. This technology
offers a 24/7 dedicated link to the Internet for a reasonable cost and no phone
charges. Most major areas in Colombo have been covered by ADSL and some suburbs
as well. This would be a great benefit when planning the IT solution for Mount
Shipping.
The Sri Lanka Ports Authority [1]
MARINET All Shipping Agents are involved in
Container Handling Activities numbering approximately 30. They are connected
electronically with the Sri Lanka Ports Authority (SLPA) computer through the
MARINET system. The MARINET facility provides access for inquiry and provides
facilities to download the Terminal Departure report and the Bay Plan. It is
the intention of the SLPA to link up all document clearing agencies
electronically including freight forwarders, banks, exchange control, import
control, insurance companies etc. to provide an efficient service. The suppler
of the container handling software has been contacted with respect to the
implementation of several message formats. This would be of immense importance
to Mount Shipping when introducing and integrating technology.
Conclusion
The number of macro-environment factors is virtually unlimited. In practice the firm must prioritize and monitor those factors that influence its industry. It is difficult to forecast the future and the trends with a high level of accuracy. Thus, the firm must strategically plan based on the above findings.
5.2 SWOT
ANALYSIS
SWOT
analysis is a tool for auditing an organization and its environment. It is the
first stage of planning and helps marketers to focus on key issues.
Strengths and weaknesses are internal factors.
Opportunities and threats are external
factors.
Strengths
Mount
Shipping is located in a central business area in Colombo. It can be easily
visited by the customers.
Weaknesses
There
is currently almost no marketing conducted at Mount Shipping.
The
services offered are undifferentiated since the majority of the competitors
offer equal or better services.
Customer retention is weak since there is no special
catering done to the regular customers.
Opportunities
The
Internet and SMS technologies are on the rise in Sri Lanka. These technologies
could be exploited to enhance and add value to the processes.
Integration
with the Sri Lankan Port Authority system for simple electronic documentation
clearance.
Mount Shipping is still not a member of Sri Lanka’s Freight Forwarding Association. Therefore, Mount Shipping should seize the opportunity to be recognized as a leading freight-forwarding firm.
Threats
The
competitors are constantly inventing new ways to attract customers:
- Prices are lowered by the
competitors.
- The competitor comes up with a new
innovative service.
- Competitors have superior access to
the shipping lines.
Unfavourable
taxations could be introduced in the future causing a major setback.
6.0 ADOPTING AN ORGANIZATIONAL HORSEPOWER STRATEGY
Organizational
Horsepower (OHP) is a measure of
organizational competitiveness generated through organizational force and
speed. Together they provide a
framework for evaluating how various strategies can empower a business
organization.
Organizational force – is meeting as many customers’ expectations
as possible so that the firm can gain a competitive edge over its competitors.
Organizational speed – is meeting customer expectations quickly,
preferably before the competitors.
In order for Mount Shipping to attain
streamlined organizational horsepower, it would have to provide the
best-perceived perfect service at the customer’s moment of value.
The perfect service defined by the customer –
- Getting a
consignment approved in the most convenient manner.
- Constant
updates and tracking of the consignment, at the customer’s convenience.
- Painless
payment and credit checking process.
This competitive advantage does not last very
long. The only true sustainable
competitive advantage is the one that is constantly renewed. Successful firms foster innovation to
provide this renewal.
Strategic goals of the organization –
- Preparing the
documentation with maximum efficiency and effortlessness.
- Instantaneous
selection of shipping lines.
- Preparing
payments rapidly.
- Providing
feedback and answering inquiries instantly with minimum hassle.
If these strategic goals are accomplished, a
wide number of customer expectations would be met (force) and they would be
achieved swiftly (speed).
Information Technology is the essential enabler
to achieve the desired OHP level –
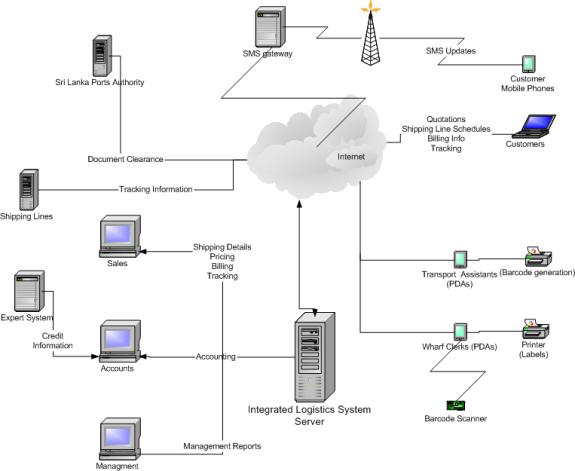
- A total
Enterprise Resource Planning Software solution
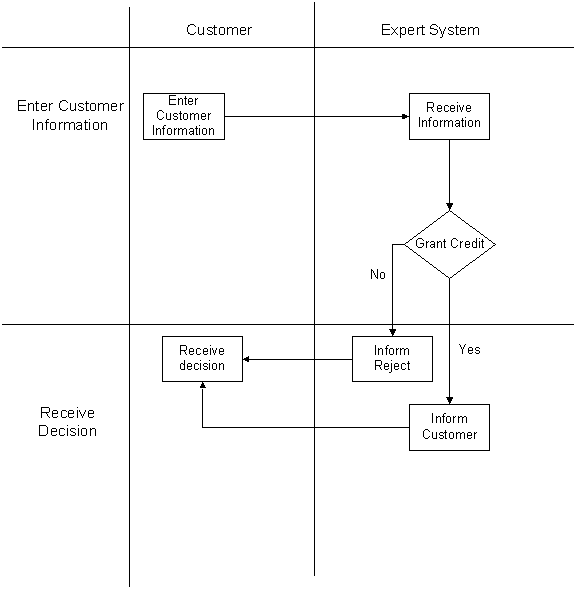
- An expert
system to decide on the shipping line based on the customers’
requirements.
- Wireless
devices to constantly provide feedback and update the customer about the
consignment from wherever the agents may be located.
- Documentation
done at customer’s convenience through the Internet.
Strategies for increasing OHP
1.
Just-in-time approach –
producing or delivering a product or service when the customer wants it. JIT generates strong organizational speed
through quick customer response but it generates very little organizational
force.
2.
Teams in an organization – a
group of people with a shared goal and task interdependence. Teams generate strong organizational force
but little organizational speed.
3.
Information Partnerships –
An agreement between organizations for the sharing of information to strengthen
each partner in the organization. By sharing strategic information, these
partnerships can generate both organizational force and speed
4.
Timeless & Locationless operations – operate without regard to time or location. These are essentially companies that have introduced most of
their services through the Internet. They are timeless since these companies
operate 24hrs a day using IT systems.
They generate organizational speed through quick, timely customer
response. This generates organizational
force by allowing the organization to reach more customers. Jointly the timeless & locationless
organizations generate both force and speed
5.
The transnational firm –
produces and sells products and services all over the world in coordinated
cooperation. All operations share
information and resources, using IT networks. Since this sort of firm receives
a lot of international exposure, remarkable organization force and speed is
generated.
6.
Virtual Organization – A
network of independent organizations linked together by IT to exploit market
opportunities by sharing skills, costs, and market access. Generates a great deal of organizational
speed.
7.
The learning organization –
An organization whose people are continually discovering how to learn together
while simultaneously altering their organization with the knowledge that they
have gained. They invent new strategies for serving the customers internally,
based on its own knowledge of their customers.
Organizational speed is the main focus.
Mount Shipping can adopt a combination of OHP strategies to streamline the organization’s force and speed:
- Just in time –
Organizational force can be increased by meeting as many customer
expectations by providing the service for the customer when he/she
requires it.
2. The information Partnership – Mount Shipping can increase its organizational force and speed by using an IT system to integrate with the Sri Lanka Ports Authority system and the shipping lines’ systems.
3.
Timeless & Locationless Operations
– Customers should be attended to at their own convenience, regardless of the
time. This is achievable through the use of the World Wide Web. The travelling
agents do not have travel back and forth to the head office as IT technology
could be used to communicate from various parts of the country.
Quality
Quality is a foundation for OHP. Quality is
meeting the customers’ expectation so it is they who define the quality of the
service. They expect a perfect service
when, where and how they want it. They dictate the terms and if their desires
are fulfilled, the firm would thus be providing a high quality service. Mount
Shipping is currently offering nothing special that would deter customers from
their competitors. They simply offer a basic service and present no particular
reason for a customer to choose them from the myriad of other freight-forwarding
firms. This is where BPR comes into play and is required to increase the
quality of the service, increase productivity and reduce the cost.
The 3 C’s -
- Customers are
powerful
- Change is
constant
- Competition has
intensified
These are the main drivers of a business
reengineering effort and were highlighted in the previous sections of this
document.
7.0 BENCHMARKING
Benchmarking can be simply defined as searching and finding out the best practices for a particular work. The technique of the benchmarking is to identify the performance and success of other organization’s and how it applies to our organization’s process. The comparing of organizations may be performing in very different areas but the concept is that we have to consider the success of the particular organization.
The first step is to identify the processes, which requires benchmarking of the organization. Study of the particular section and related area are also vital for the benchmark. Analyze the process of other organizations and their performance is important to make the solution and the best practice.
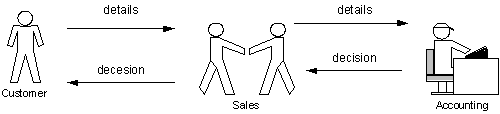
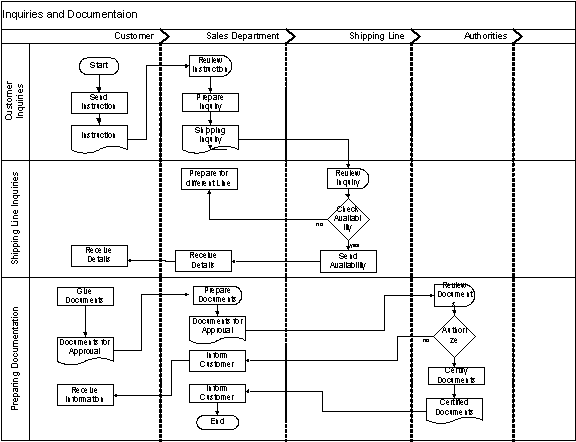
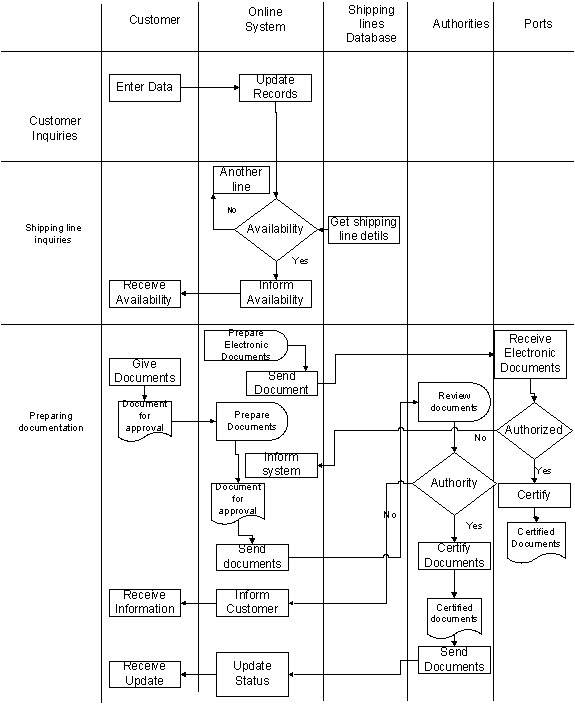
The freight-forwarding department of the Mount shipping agencies (Pvt) Ltd, there are some sections requires benchmarking and reengineer. The inquiries and the documentation process of Mount shipping having some problems and it is time consuming process. The customer inquiries and documentation process is directly relates to the customer satisfaction about the organization as well. The competition of this industry is much higher and the customer response time is key aspect in this field. The current procedure of handling customer inquirers is not up to standard and takes much time comparing with the other processes of the company.
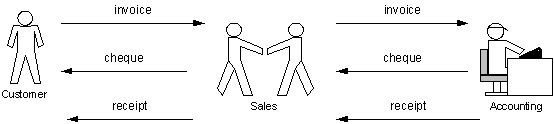
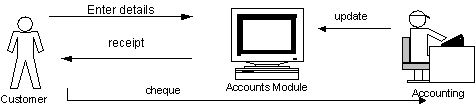
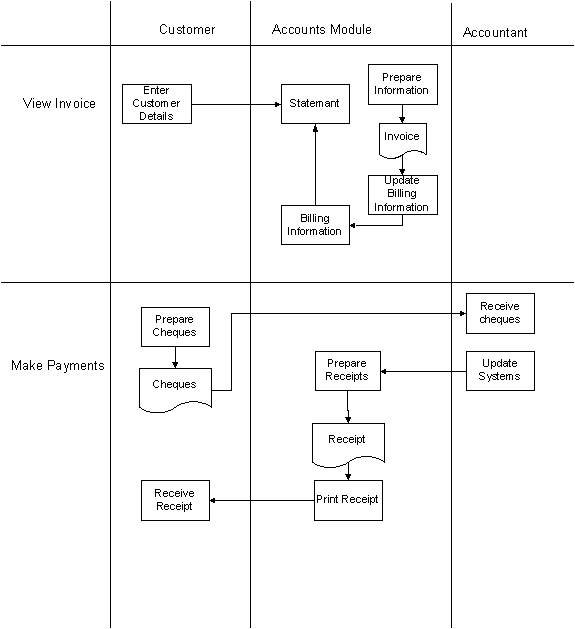
The credit handling process of the Mount shipping agencies face some problems because the customers are not informed about their credit period on time. Currently Mount Shipping keeps their customer payment records manually. Customers have to forward their payment cheques to the sales assistance and he/she responsible to issue payment receipt and inform the accounts department. In some cases, it will take some time to the inform accounts department and update the customer statement of accounts. Customers receive their statement of accounts monthly from the account department with out updating payments, which are recently settled. This problem also leads to reduce accuracy of the credit facility. Sometimes customer exceeding their credit period are accepted by Mount shipping and because the accounts department does not having up to date information about the customer payments. In some cases, customers have already settled their payments according to the credit facility but there are some problems in dispatching their cargo from the yard.
Currently, Mount shipping agencies are not having online tracking system to view the status of the consignment. The sales assistant will be able to inform the status of the particular shipment to the customer. In some cases, the customers have to remind the sales assistance to check the status of their consignment.
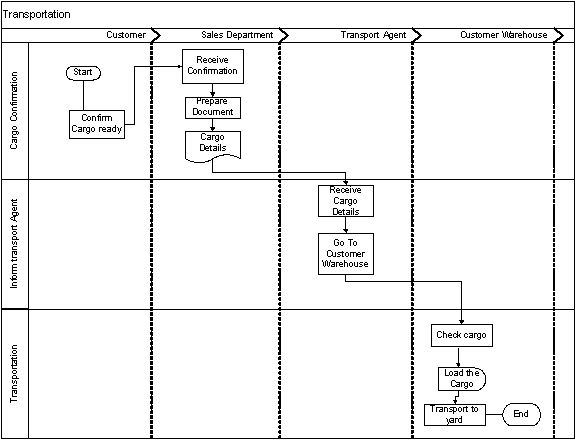
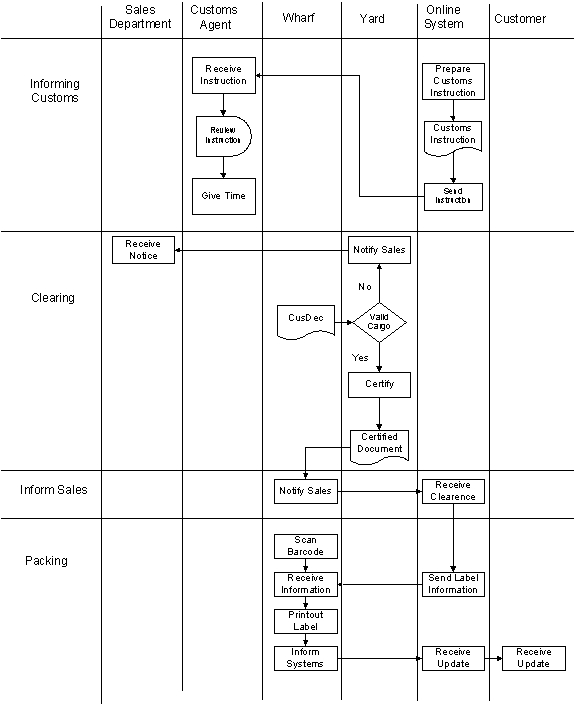
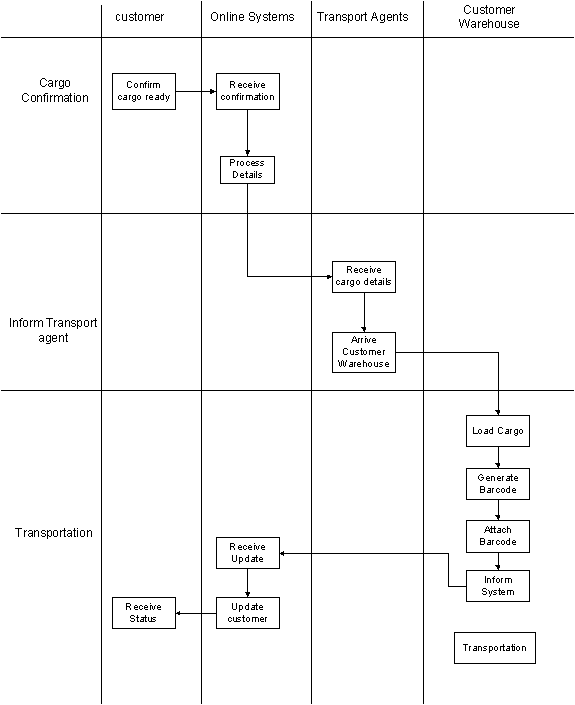
Mount Shipping agencies are not having their own yard and they using external yard owned by Asha shipping lines. The facilities available for Mount Shipping wharf clerk are very limited. Normally a sales assistant has to inform about the shipping details to the wharf clerk and he is responsible to follow the instruction provided by them. The consolidate shipments having cargo owned by different customers and wharf clerk have to careful in labelling the cargo provided by the sales department. Finally, Mount Shipping has the responsibility to handle the cargo accurately and cargo should be received to the consignee on time. The labelling and loading of the cargo is also vital and it has to be accurate.
Solutions
The competition companies of Mount shipping lines are able to reply to their customers within a short period of time. For Example, John Keells Holdings Mack International freight services are able to process and confirm the customer inquiries more efficiently than the Mount shipping lines. The confirmation of the consignment is important in the customer’s point of view. For the regular customers of the Mack International freight services do not require to forward their consignee details repeatedly as Mount Shipping and they will receive the confirmation on time.
The credit handling process of the Mount shipping lines is very inefficient compared with the other competition freight forwarding companies. The invoice value of each consignment is higher and minimum range is six hundred to eight hundred US Dollars. The competition companies are highly concerned with the credit period of each customer and they immediately inform after it exceeds the credit period. One competitive company of Mount shipping is Aiken Spence Ace Cargo freight services. This is one of the freight forwarding companies that are concerned with the customer credit period and they will immediately inform up to date information to the customers prior to the shipment. They are updating payments records as soon as customer settles the payments to minimize the customer dissatisfaction.
Most of the freight forwarding companies has online shipment tracking systems and customers will be able to view the status of the shipment by logging into the company website. Mitsui O.S.K freight services having a proper online shipment tracking system and it has lead to an increase in customer satisfaction.
8.0 BPR METHODOLOGY COMPARISON
8.1 CLEAN
SHEET APPROACH
Basic questions to be answered
·
What underlying needs are we trying to satisfy and for
whom?
·
Why are we trying to satisfy those needs? Does it fit with
the organization strategy?
·
Where do these needs need to be serviced?
·
When are we required to meet those needs?
·
How will we deliver the above?
·
What would the company expect if the service was
contracted out?
This
approach is used if the company is willing to take risks. Especially companies
who are failing use this approach.
Step1 – Gain a high level
understanding of the existing processes. Understand the core processes and
what outcome they deliver. Normally there are 6 – 8 core processes that may be
identified. The key stages of each of these processes will be studied.
Step2 – Benchmarking,
brainstorming, fantasizing. Alternative ways of working should be identified.
Consider the customer’s point of view. Totally new ideas, which may not sound
normal, may surface. Those ideas should not be dismissed too quickly, but have
to be considered carefully. Ideas that look more appropriate should be analyzed
in depth.
Step3 – Process design. Highly
iterative. Should not revert back to the traditional way of doing things. The
ideas that were chosen through brainstorming will be thought in more detail.
Human capabilities in the new working environment and technological
capabilities will be considered. When the ideas are being translated into
design special note should be taken that the ‘service task’ is considered in
some detail.
Step4 – Validate. Validate
the design by simulating how it will operate in the real world. Any exceptions
should not be considered invalid but handled as such the process dealing with
the majority of cases. The ESIA rule should be applied to his new process to
ensure it is optimal in terms of delivering the desired outcomes along the
dimensions of effectiveness, efficiency and adaptability. Use process maps.
8.2 Rapid
Reengineering
Rapid Re is a five stage, reengineering methodology developed by Manganelli. These stages are similar to that of Davenport’s methodology but delves into more detailed about process modeling. Manganelli pays more emphasis to entities rather than processes and his attention is towards improving existing processes.
In Manganelli’s book, Reengineering Handbook describes the Rapid Re 5 stage methodology.
- Preparation
- Identification
- Vision
- Design - technical, social
- Transformation
These 5 stages are further broken down to 54 steps (Figure 1) that enables organizations to achieve swift, substantive results by making radical changes in strategic value-added business processes.[3]
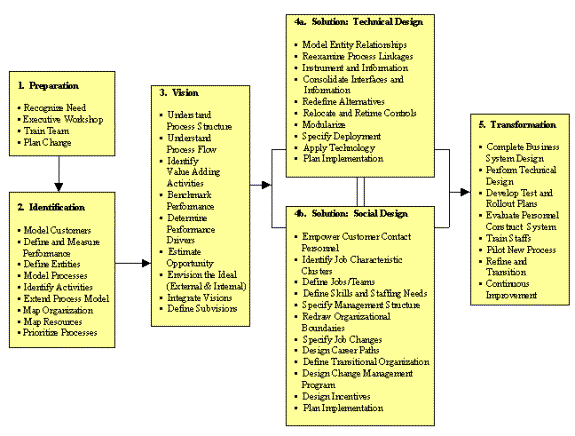
Figure 1: The Rapid Re Methodology
Stage 1: Preparation
The preparation stage is the starting point for the Rapid Re methodology. This stage focuses on setting up of the business goals and objectives, aligned with the vision of the company, which are agreed upon by the senior management of the organization. Further, project parameters such as cost, time, and resources are established. Identification of the re-engineering team and proper training is given and the initial change management plan is developed at this stage.
Stage 2: Identification
The objective of this stage is to identify and develop an understanding about the business customer oriented process model. Identification produces definitions of customers, process and performance measures, and identifies value-adding processes [2]. The deliverables at this stage includes organizational process maps, resource lists, volume, and frequency of data. This stage involves nine tasks:
- Model Customers
- Define and Measure Performance
- Define Entities
- Model Processes
- Identify Activities
- Extend Process Model
- Map Organization
- Map Resources
- Prioritize Processes
Stage 3: Vision
Creating an process vision is vital for BPR in order to achieve dramatic improvements, its how BPR is distinguished from other methodologies. This stage involves innovative, creative thinking to develop the new process, which will achieve breakthrough performance. This stage identifies, current process elements, problems and issues; comparative measure of current process performance, improvement opportunities and objectives [1]. This stage involves 10 tasks:
·
Understand Process Structure
·
Understand Process Flow
·
Identify Value-adding Activities
·
Benchmark Performance
·
Determine Performance Drivers
·
Estimate Opportunity
·
Envision the Ideal (External)
·
Envision the Ideal (Internal)
·
Integrate Visions
·
Define Sub visions
Stage 4A: Solution – Technical Design
This stage will focus on the technical aspects of the new processes. The specifications at this stage will produce descriptions of technology, standards, procedures, etc [1]. The ten steps in this stage are:
- Model Entity Relationships
- Re-examine Process Linkages
- Instrument and Informate
- Consolidate Interfaces and Information
- Redefine Alternatives
- Relocate and Retime Controls
- Modularize
- Specify Deployment
- Apply Technology
- Plan Implementation
Stage 4B: Solution – Social Design
Its important to focus on the social aspects such as human resource of the organization as BPR will restructure the organization to meet is new goals. This stage is a twelve-step stage:
- Empower Customer Contact Personnel
- Identify Job Characteristic Clusters
- Define Jobs/Teams
- Define Sills and Staffing Needs
- Specify Management Structure
- Redraw Organizational Boundaries
- Specify Job Changes
- Design Career Paths
- Define Transitional Organization
- Design Change Management Program
- Design Incentives
- Plan Implementation
Stage 5: Transformation
The purpose of the final stage of this process is to realize the process vision. This stage produces pilot and full production versions of the reengineered processes and continual change management [3].
- Complete Business system Design
- Perform Technical Design
- Develop Test and Roll-Out Plans
- Evaluate Personnel
- Construct system
- Train Staff
- Pilot New Process
- Refine Transition
- Continuous Improvement
8.3 Systematic Redesign
Systematic Redesign is another method
that can be use to Re engineer the business Processes in a company. Redesigning
an existing process is about making it better cheaper and faster. The objective
of every organization is that all it’s activities should add values in some way
to the customer. When redesigning is done it is important to eliminate all non
value adding activities and the stream lining of the core value adding ones.
The rule for this is called ESIA.
- Eliminate
- Simplify
- Integrate
- Automate
Eliminate
Where process thinking is new, a large number of activities is found to be non value adding. All these non value-adding steps should be eliminated.
E.g.: Waiting time, Duplication and Reconciling.
Simplify
After the elimination of non value adding tasks this essential to simplify the remaining tasks.
Eg: Forms, Problem Areas, and Procedures.
Integrate
The tasks that have been simplified in the above step has to be put together to effect a smooth flow in delivery of the customer requirements.
Eg: Jobs, Team, and Customers.
Automate
It is very important to see whether the process is problematic before automating because automation can often make matters worst. Therefore automation should be applied after elimination, simplification and integration.
Eg: Data capture, Data transfer and Data analysis.
An advantage of this approach is that change can be made
incrementally and thus quickly, in small parts, which reduces the risk. A
disadvantage is that the change is based on the existing process and an
innovative new approach is less likely to surface. It focuses on continuous
improvement.
8.4 Methodology Comparison [4]
|
|
Step 1: Project
Preparation |
Step 2: Redesign
of Processes |
Step 3: Implementation
|
|
Hammer/Champy (Consultants / Academics) |
1.
Introduction 2. Identification 3. Selection |
4.
Understanding 5. Redesign |
6.
Implementation |
|
Davenport (Academic) |
1.
Visioning and Goal setting 2. Identification |
3.
Understand and measure 4. Information Technology |
5.
Prototyping 6. Implementation |
|
Manganelli/Klein (Consultants) |
1.
Preparation 2. Identification |
3.
Process Vision 4a. Technical Design 4b. Social Design |
5.
Transformation |
8.5 Justification
of the Chosen Methodology
Systematic redesign considers the existing processes and allows to make the changes one by one. In this approach, change can be made incrementally and thus quickly, in small parts, which reduces the risk. These improvements can be done in a massive scale to bring about the right changes. Many European automotive component producers have experienced massive incremental change with a large number of small changes been implemented which adds up to significant improvement performance. This approach gives the feature of continues improvement to ensure that the company does not lose their competitive edge. Role of automation in systematic redesign is an enabling one.
Mount shipping agencies is a company that is relatively new to the industry. Currently they face many limitations when carrying out operations. The company mainly focuses on Sea-Air freight handling. The cargo is transported from gateway of Dubai via British Airways flights only. The reason being they are the only airline who offers a lower rate. Another limitation is not having a yard of their own. They currently use the yard, which belongs to Asha shipping lines.
Since the company is not willing to take a large risk of entirely changing its processes, a clean sheet approach would be detrimental. Since we have to redesign the processes within these confinements, a systemic approach would be ideal. This approach allows to carefully eliminate, simplify integrate and automate the tasks. Thus, it would facilitate a careful redesign of the processes. It would also provide for continuous improvement in the future.
|
ELIMINATE |
SIMPLIFY |
INTEGRATE |
AUTOMATE |
|
Waiting time in inquiries |
Accounting procedure |
Credit check |
Retrieve shipping line details |
|
Document Duplication |
Credit check procedure |
Inquiries |
Cargo details to wharf |
|
Query shipping details |
|
Availability |
Customer updates |
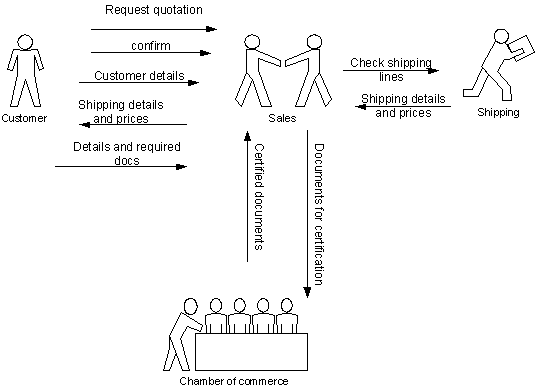
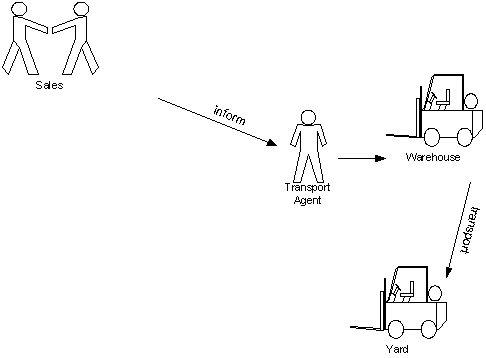
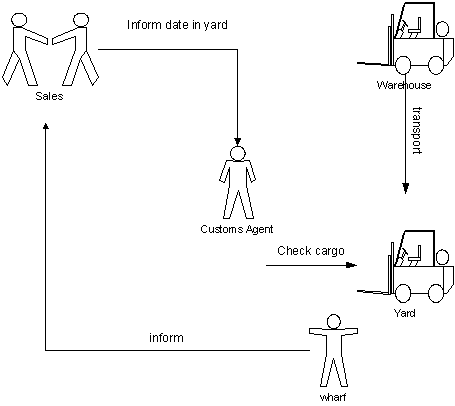
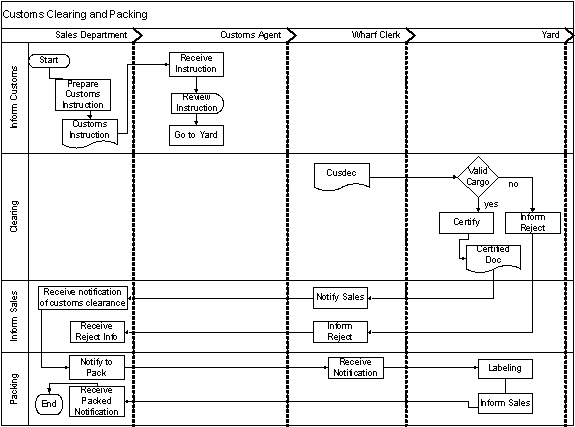
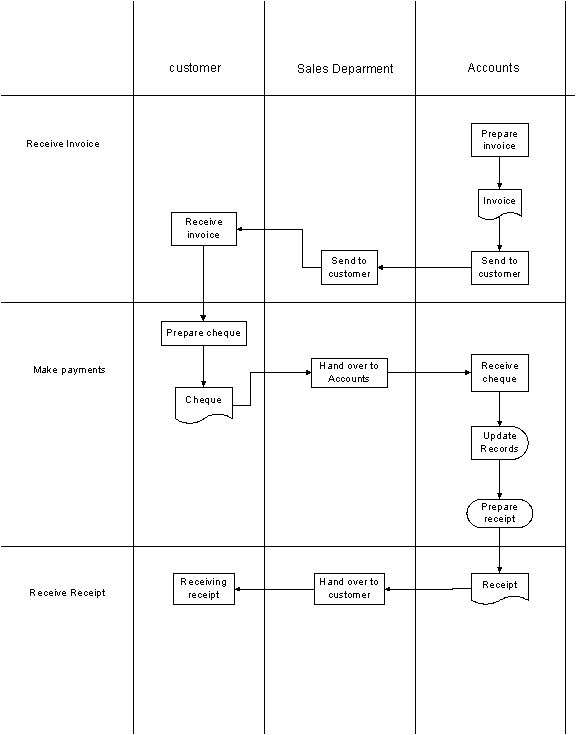
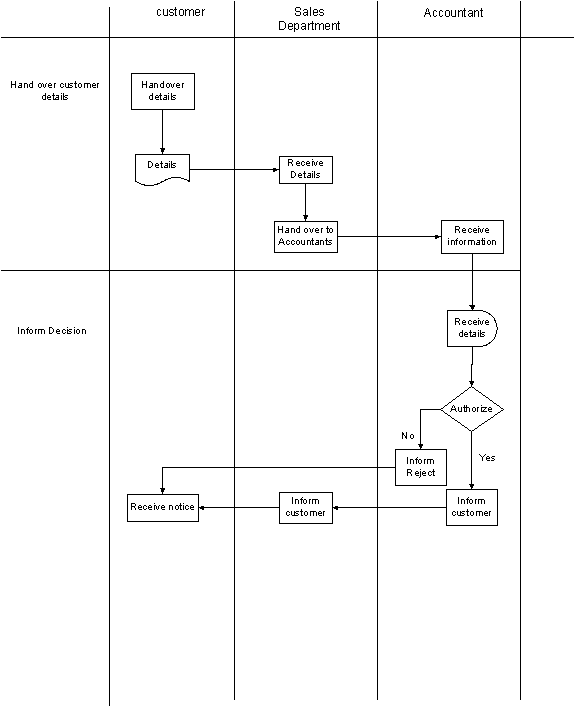
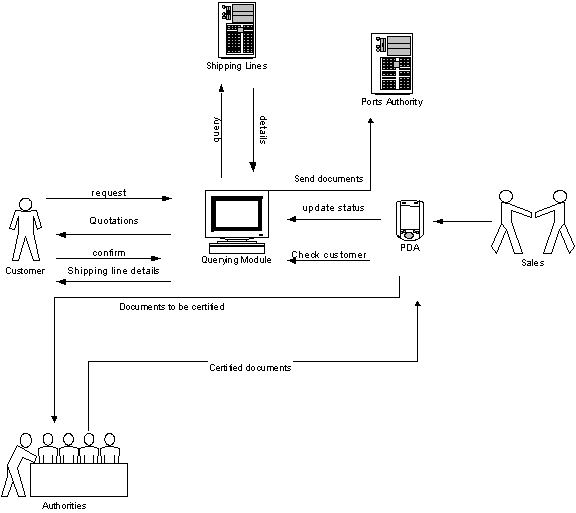
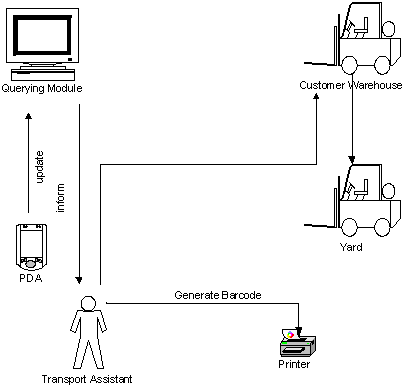
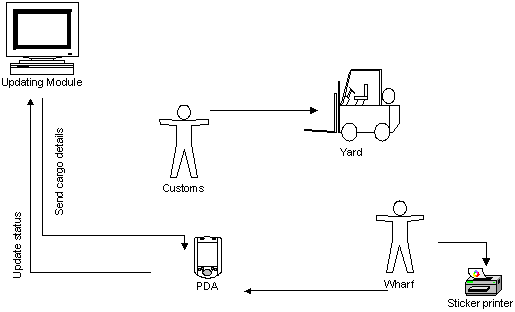
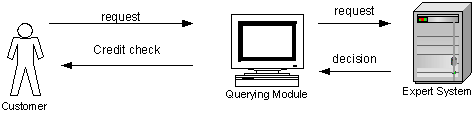
9.0 AS-IS PROCESS ANALYSIS
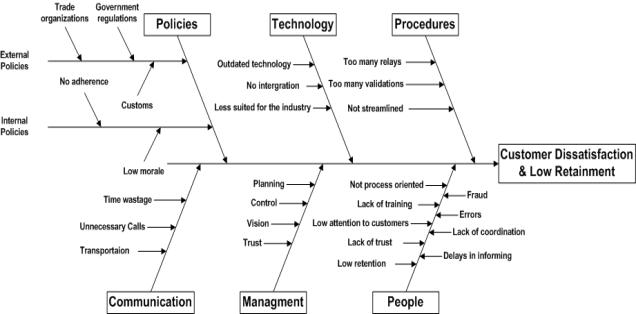
9.1 Cause and Effect Diagram
(Fishbone)